日期:2025年 06月 21日
標籤: C# Asp.NET Core Windows Forms
摘要:個人作品
應用所需:1. Visual Studio 2022
程式說明:使用 Dotnet 8.0 實作 C# WindowsForm - 康威生命遊戲的小作品
範例檔案:Githu連結
基本介紹:本篇分為 3 大部分。
第一部分:康威生命遊戲簡介
第二部分:程式說明
第三部分:Demo成果
第一部分:康威生命遊戲簡介
Step 1:起源
可以參考 Wiki
起源背景
康威生命遊戲由英國數學家約翰·霍頓·康威(John Horton Conway)在1970年發明。
他的靈感來自於數學家約翰·馮·諾伊曼(John von Neumann)在1940年代提出的自我複製機器概念。
康威想要創造一個比馮·諾伊曼的模型更簡單,但仍能展現複雜行為的系統。經過大量實驗,他設計出這套只需要三條規則的細胞自動機。
開放使用 - 康威本人從未試圖對此主張任何商業權利,而是鼓勵大家自由探索和應用
Step 2:遊戲規則
生命遊戲在無限大的二維格子上進行,每個格子代表一個「細胞」,有兩種狀態:
| 活細胞(通常用黑色或實心表示) |
| 死細胞(通常用白色或空心表示) |
如果以程式的角度來看就是布林,細胞不是 True 就是 False
並且基於以下 3 條規則,驅動整個遊戲
| 每個細胞的下一代狀態由其周圍8個鄰居的狀態決定: |
| 1. 生存規則: 活細胞周圍有2或3個活鄰居時,下一代繼續存活 |
| 2. 死亡規則: 活細胞周圍活鄰居少於2個(孤獨死)或多於3個(過度擁擠死)時,下一代死亡 |
| 3. 誕生規則: 死細胞周圍恰好有3個活鄰居時,下一代復活 |

Step 3:遊戲規則 - 圖示
| 1. 生存規則:活細胞周圍有2或3個活鄰居時,下一代繼續存活 |

方塊細胞,由於每個細胞身邊的鄰居都為 2 ,因此下一世代存活
| 2. 死亡規則:活細胞周圍活鄰居少於2個(孤獨死)或多於3個(過度擁擠死)時,下一代死亡 |

中間的 1 個細胞其餘 8 個鄰居都沒有活細胞,因此下一世代也死亡

| 3. 誕生規則:死細胞周圍恰好有3個活鄰居時,下一代復活 |

中間的 1 個死亡細胞有 3 個鄰居,因此下一世代復活
※左邊的細胞因為有 2 個活鄰居因此下一世代存活

Step 4:補充說明 - 零玩家遊戲
可以參考 Wiki
零玩家遊戲(英語:zero-player game,no-player game)是由無意識玩家所進行的遊戲。
在電腦遊戲中,這個詞是指玩家為使用人工智慧的程序,而不是真正的人類[1]。
此外,有些策略和棋牌遊戲可以讓程序的AI自動代理,也可以說是零玩家模式的遊戲。
Step 5:應用範圍 - 技術開發
在軟體開發中,最常使用到這些地點,本篇是 C# 代碼對於程序化生成的基本實現。
| 程序化生成 | 遊戲開發中用於生成地形、迷宮或其他隨機內容 |
| 效能最佳化練習 | 是測試和改進演算法效率的理想平台,可以嘗試各種最佳化技巧 |
| 平行處理實驗 | 由於每個細胞的計算相對獨立,適合練習多執行緒或GPU程式設計 |
第二部分:程式說明
Step 1:範例專案說明
| 1. GameOfLife | : | 主程式,實現康威生命遊戲的核心代碼 |
| 2. MainForm.cs | : | 程式進入點 |

Step 2:GameOfLife 主代碼
核心代碼主要有 6 大流程
| 1. 初始化配置 | : | 主程式的初始化配置 |
| 2. 載入 Winform 觸發 | : | 載入 Winform 時,呼叫主程式 |
| 3. 配置細胞與執行 | : | 將配置的細胞寬、高設定,此範例是 256 * 256 個細胞 |
| 4. 背景生命週期 | : | 每 100 ms 觸發一次生命週期,每個細胞都是獨立的,也就是每秒會運算 655360 次 |
| 5. 更新 WinForm 畫面 | : | 畫面渲染到 Winform 上 |
| 6. 縮放畫面比例 | : | 依照配置比例讓 UI 縮放 |
public partial class GameOfLifeForm : Form
{
private const int WidthCells = 256;
private const int HeightCells = 256;
private const int CellSize = 2;
private byte[,] current;
private byte[,] next;
private Bitmap bitmap;
private Timer timer;
public GameOfLifeForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitialThisForm();
// 1. 初始化配置
void InitialThisForm()
{
// 根據縮放比例調整視窗大小
this.ClientSize = new Size(WidthCells * CellSize, HeightCells * CellSize);
// 初始化畫面
this.DoubleBuffered = true;
this.Text = "Game of Life (CPU Only)";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 2-1. 載入 Winform 觸發
/// </summary>
private void GameOfLifeForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//2-2. 執行 CPU 運算的 Game Of Life
GameOfLifeCpu();
}
/// <summary>
/// 3. 實際代碼
/// </summary>
public void GameOfLifeCpu()
{
// 3-1. 初始化資料,決定像素數量 WidthCells * HeightCells
current = new byte[WidthCells, HeightCells];
next = new byte[WidthCells, HeightCells];
Random rand = new();
// 3-2. 初始化配置每個細胞 生 與 死
for (int xAxis = 0; xAxis < WidthCells; xAxis++)
{
for (int yAxis = 0; yAxis < HeightCells; yAxis++)
{
current[xAxis, yAxis] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() > 0.7 ? 1 : 0);
}
}
// 3-3. 建立放大後的 bitmap
bitmap = new Bitmap(WidthCells * CellSize, HeightCells * CellSize, PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb);
// 3-4. 設定定時更新
timer = new Timer { Interval = 100 };
timer.Tick += (s, e) => Step();
timer.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// 4. 背景的 Timer 持續執行該方法 Interval 決定觸發的生命週期
/// </summary>
private void Step()
{
// 4-1. Game of Life 計算
// 備註: xAxis, yAxis 代表細胞座標
// 備註: gridX, gridY 代表鄰居偏移量
for (int yAxis = 0; yAxis < HeightCells; yAxis++)
{
for (int xAxis = 0; xAxis < WidthCells; xAxis++)
{
// 4-2. 以當前細胞為基準點,計算鄰居數量
int count = 0;
for (int gridY = -1; gridY <= 1; gridY++)
{
for (int gridX = -1; gridX <= 1; gridX++)
{
if (gridX == 0 && gridY == 0)
continue;
// ※處理邊界(環繞)
int nx = (xAxis + gridX + WidthCells) % WidthCells;
int ny = (yAxis + gridY + HeightCells) % HeightCells;
count += current[nx, ny];
}
}
byte alive = current[xAxis, yAxis];
// 4-3. Game of Life 規則
if (alive == 1 && (count < 2 || count > 3))
next[xAxis, yAxis] = 0; // 死亡
else if (alive == 0 && count == 3)
next[xAxis, yAxis] = 1; // 誕生
else
next[xAxis, yAxis] = alive; // 保持原狀
}
}
// 4-4. 將新的生命週期細胞狀態替換 current / next
(current, next) = (next, current);
// 4-5. 更新畫面
DrawBitmap();
Invalidate();
}
/// <summary>
/// 5. 更新到 Bitmap 上
/// </summary>
private void DrawBitmap()
{
BitmapData data = bitmap.LockBits(
new Rectangle(0, 0, WidthCells, HeightCells),
ImageLockMode.WriteOnly,
PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb);
unsafe
{
byte* ptr = (byte*)data.Scan0;
int stride = data.Stride;
for (int yAxis = 0; yAxis < HeightCells; yAxis++)
{
for (int xAxis = 0; xAxis < WidthCells; xAxis++)
{
int value = current[xAxis, yAxis] * 255;
ptr[yAxis * stride + xAxis * 3 + 0] = (byte)value; // B
ptr[yAxis * stride + xAxis * 3 + 1] = (byte)value; // G
ptr[yAxis * stride + xAxis * 3 + 2] = (byte)value; // R
}
}
}
bitmap.UnlockBits(data);
}
/// <summary>
/// 6. 觸發畫 BitMap 時
/// </summary>
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e)
{
if (bitmap != null)
{
// 6-1. 使用最近鄰插值來保持像素的清晰度
e.Graphics.InterpolationMode = System.Drawing.Drawing2D.InterpolationMode.NearestNeighbor;
e.Graphics.PixelOffsetMode = System.Drawing.Drawing2D.PixelOffsetMode.Half;
// 6-2. 繪製
e.Graphics.DrawImage(bitmap,
new Rectangle(0, 0, WidthCells * CellSize, HeightCells * CellSize),
new Rectangle(0, 0, WidthCells, HeightCells),
GraphicsUnit.Pixel);
}
}
protected override void OnFormClosed(FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
base.OnFormClosed(e);
timer?.Stop();
timer?.Dispose();
bitmap?.Dispose();
}
}

第三部分:Demo成果
Step 1:進入點
程式打開後,陽春的執行按鈕
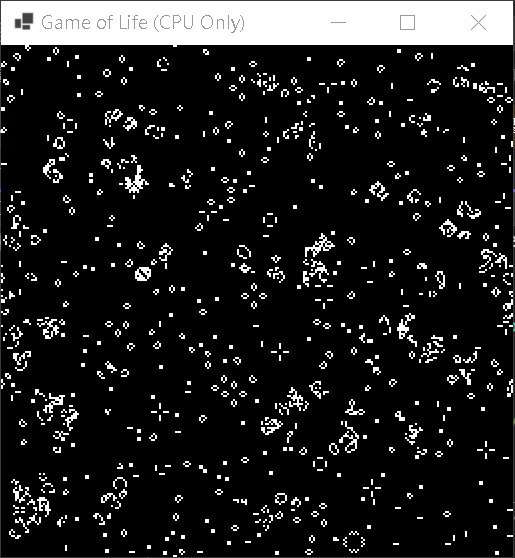
Step 2:Demo 最初世代細胞
最初的畫面,會將 65536 個細胞隨機分配生、死

Step 3:Demo 無止盡的輪迴
在經歷過無限的世代後,細胞若處於震盪狀態會持續存活
彷彿永遠有生命流動