日期:2024年 08月 17日
標籤: Algorithm String Searching Algorithm C# Asp.NET Core
摘要:演算法-字串搜尋
m:找尋字串總長度 ; n:文本總長度 ; σ是字符集的大小(例如,ASCII字符集的大小为256)
時間複雜度(Time Complex):O(m) ~ O(m * n)
最佳時間: O(m)
平均時間: O(n / m)
最壞時間: O(m * n)
空間複雜度: O(m + σ)
範例檔案:Source Code
範例專案:Code Project
基本介紹:本篇分為4大部分。
第一部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 介紹
第二部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 實現&圖解:壞字符表
第三部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 實現&圖解:好後綴表
第四部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 實現&圖解:完整版本
第一部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 介紹
Step 1:簡介
以下截取於Wiki
在電腦科學里,博耶-穆爾字串搜尋演算法是一種非常高效的字串搜尋演算法。它由羅伯特·史蒂芬·博耶和J·斯特羅瑟·穆爾設計於1977年。
此演算法僅對搜尋目標字串(關鍵字)進行預處理,而非被搜尋的字串。
雖然博耶-穆爾演算法的執行時間同樣線性依賴於被搜尋字串的大小,但是通常僅為其它演算法的一小部分:它不需要對被搜尋的字串中的字元進行逐一比較,而會跳過其中某些部分。
通常搜尋鍵碼越長,演算法速度越快。
它的效率來自於這樣的事實:對於每一次失敗的匹配嘗試,演算法都能夠使用這些資訊來排除儘可能多的無法匹配的位置。
簡言之,搜尋一串字串(文本),用此演算法大多時間都可以在線性時間,但是最壞則到了多項式時間
※來源:Wiki

Step 2:優缺點
優點具有以下:
| 1. 高效率 | : | 在平均情況下,它的時間複雜度接近於 𝑂(𝑛/𝑚),大多數實際應用中非常高效 |
| 2. 跳躍機制 | : | 算法利用了兩種啟發式方法(壞字符啟發式和好後綴啟發式),使得它在文本中可以跳過大量的字符,從而減少了不必要的比較次數。 |
缺點:
| 1. 複雜度高 | : | 需要知道如何處理壞字符和好後綴啟發式的預處理階段 |
| 2. 最壞情況性能差 | : | 在某些特定情況下(例如,當模式字串和文本有很多重複字符時),其最壞情況時間複雜度為 𝑂(𝑚⋅𝑛) |
| 3. 預處理空間開銷 | : | 構建壞字符和好後綴表需要額外的空間 O(m + σ) ※σ是字符集的大小(例如,ASCII字符集的大小为256) |
Step 3:預處理匹配表(壞字元、好後綴表) - 說明
KMP 核心是透過預先使用失配函數,產生查找字串的匹配表,讓搜尋的過程中,不用每次都從頭開始查詢。
以下出自 Wiki :
部分匹配表,又稱為失配函式,作用是讓演算法無需多次匹配S中的任何字元。
能夠實現線性時間搜尋的關鍵是在主串的一些欄位中檢查模式串的初始欄位,可以確切地知道在當前位置之前的一個潛在匹配的位置。
換句話說,在不錯過任何潛在匹配的情況下,"預搜尋"這個模式串本身並將其譯成一個包含所有可能失配的位置對應可以繞過最多無效字元的列表。
第二部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 實現&圖解:壞字符表
Step 1:建構式 - 進入
為了便於解釋演算法流程,這篇範例只說明使用[壞字符表]如何實現,由建構式開始
public BadCharacterExample(string text, string pattern)
{
Console.WriteLine("1. 第一種方式:壞字符表");
Search(text, pattern);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine();
}
Step 2:主程式 - Boyer-Moore (壞字元)
主程式拆成 8 小部分,其中第 1-3 部分 BadCharHeuristic(pattern); 會進行預處理,建立壞字元的表。
/// <summary>
/// 1-2. 執行演算法 - 搜尋指定字串
/// </summary>
private void Search(string text, string pattern)
{
int m = pattern.Length;
int n = text.Length;
//1-3. 找出壞字元表
var badchar = BadCharHeuristic(pattern);
//1-4. 開始搜尋
int currentIndex = 0;// 起始位置
int moveIndex = 0;
while (currentIndex <= (n - m))// 不可超過最大長度
{
//1-5. 從後往前比對
moveIndex = m - 1;
// 1-6. 若有不同,則移動到壞字元表的位置
while (moveIndex >= 0 && pattern[moveIndex] == text[currentIndex + moveIndex])
moveIndex--;
if (moveIndex == -1)// 1-7. 若比對到最後,則表示找到
{
Console.WriteLine("Pattern occurs at index " + currentIndex);
currentIndex += (currentIndex + m < n) ? m - badchar.GetValueOrDefault(text[currentIndex + m], -1) : 1;
}
else// 1-8. 若有不同,則移動到壞字元表的位置
{
currentIndex += Math.Max(1, moveIndex - badchar.GetValueOrDefault(text[currentIndex + moveIndex], -1));
}
}
}
Step 3:子函數 - 建立壞字元表
壞字元表是依照 pattern 的長度 - 1 產生對應的位置索引
以搜尋的字串 EXAMPLE 為例,會產生以下:
/// <summary>
/// 1-3. 建立壞字元表
/// </summary>
private Dictionary<char, int> BadCharHeuristic(string pattern)
{
var result= new Dictionary<char, int>();
for (int index = 0; index < pattern.Length; index++)
result[pattern[index]] = index;
return result;
}
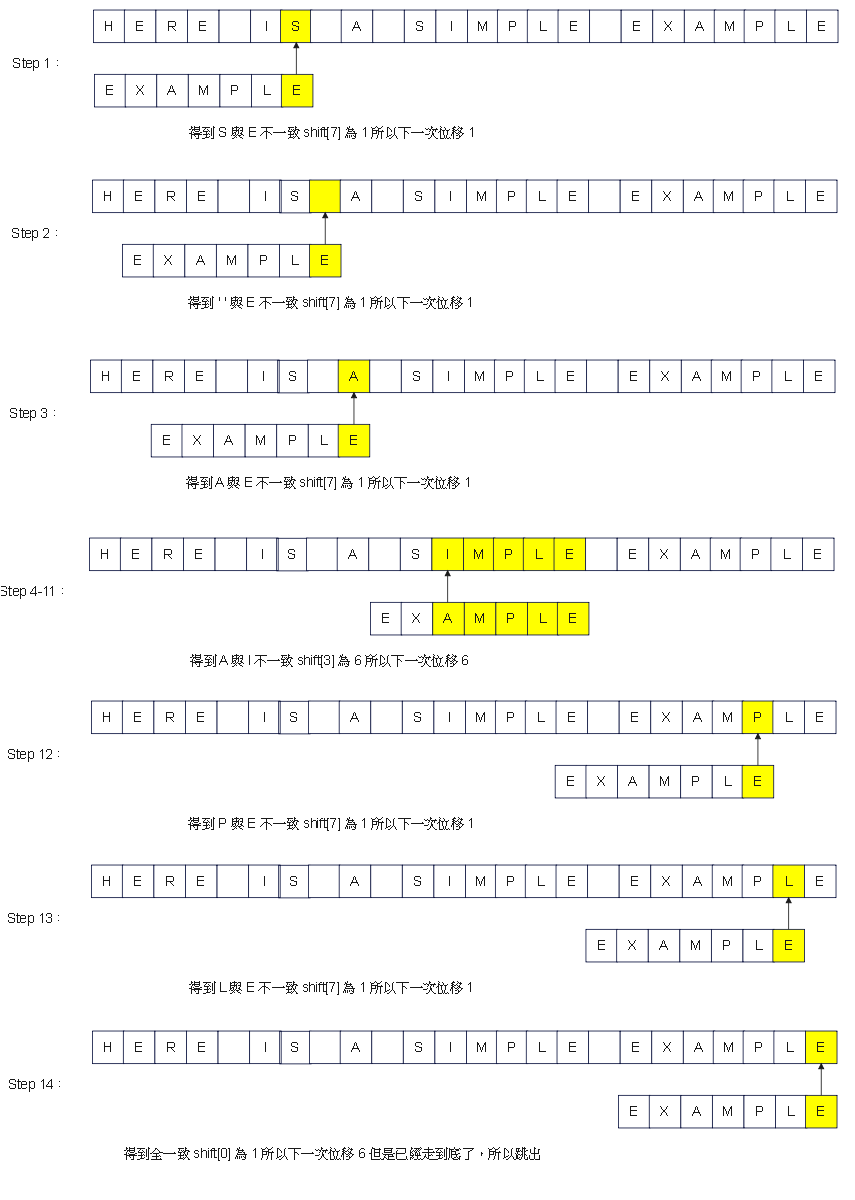
Step 4:圖解 - 1
使用文本 : HERE IS A SIMPLE EXAMPLE
搜尋字串 : EXAMPLE
壞字元表 : [6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]

第三部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 實現&圖解:好後綴表
Step 1:建構式 - 進入
為了便於解釋演算法流程,這篇範例只說明使用[好後綴表]如何實現,由建構式開始
public GoodSuffixExample(string text, string pattern)
{
Console.WriteLine("2. 第二種方式:好後綴表");
Search(text, pattern);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine();
}
Step 2:主程式 - Boyer-Moore (好後綴)
主程式拆成 7 小部分,其中第 2-2-1、2-3-1 部分會進行預處理,建立[好後綴表]。
/// <summary>
/// 2-1. 執行演算法 - 搜尋指定字串
/// </summary>
private void Search(string text, string pattern)
{
int currentIndex = 0, moveIndex = 0;
int m = pattern.Length;
int n = text.Length;
int[] bpos = new int[m + 1];//用於記錄模式串中每個位置的下一個可能的後綴位置
int[] shift = new int[m + 1];//用於記錄強後綴匹配失敗時應該跳過的位置數量
// 2-2-1. 紀錄每個位置的下一個可能的後綴位置
PreprocessStrongSuffix(shift, bpos, pattern);
// 2-3-1. 計算出可跳過的位置數
PreprocessCase2(shift, bpos, m);
while (currentIndex <= n - m)
{
// 2-4. 從後往前比對
moveIndex = m - 1;
// 2-5. 逐步匹配
while (moveIndex >= 0 && pattern[moveIndex] == text[currentIndex + moveIndex])
moveIndex--;
// 2-6. 找到時紀錄
if (moveIndex == -1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pattern occurs at index " + currentIndex);
currentIndex += shift[0];
}
else// 2-7. 未找到時使用好後綴表跳過對應位置數
currentIndex += shift[moveIndex + 1];
}
}
Step 3:子函數 - 建立好後綴表 - 1
好後綴表先產生每個位置的下一個可能的後綴位置
以搜尋的字串 EXAMPLE 為例,會產生變數 bpos 以下內容:
/// <summary>
/// 2-2-2. 當模式串中部分後綴匹配文本串時的情況。這有助於在失敗匹配時確定模式串應該向前移動多少
/// </summary>
private void PreprocessStrongSuffix(int[] shift, int[] bpos, string patten)
{
int pattenLength = patten.Length;
int index = pattenLength;
int currentIndex = pattenLength + 1;// 索引最右邊開始
bpos[index] = currentIndex;
while (index > 0)
{
while (currentIndex <= pattenLength &&
patten[index - 1] != patten[currentIndex - 1])
{
if (shift[currentIndex] == 0)
shift[currentIndex] = currentIndex - index;
currentIndex = bpos[currentIndex];
}
index--; currentIndex--;
bpos[index] = currentIndex;
}
}
Step 3:子函數 - 建立好後綴表 - 2
然後再計算出可跳過的位置數,此結果就是好後綴表
以搜尋的字串 EXAMPLE 為例,會產生變數 shift 以下內容:
/// <summary>
/// 計算出可跳過的位置數
/// </summary>
private void PreprocessCase2(int[] shift, int[] bpos, int m)
{
int index, moveIndex;
moveIndex = bpos[0];
for (index = 0; index <= m; index++)
{
if (shift[index] == 0)
shift[index] = moveIndex;
if (index == moveIndex)
moveIndex = bpos[moveIndex];
}
}
Step 5:圖解 - 1
使用文本 : HERE IS A SIMPLE EXAMPLE
搜尋字串 : EXAMPLE
好後綴表 : [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 1]
好後綴表變數名稱:shift
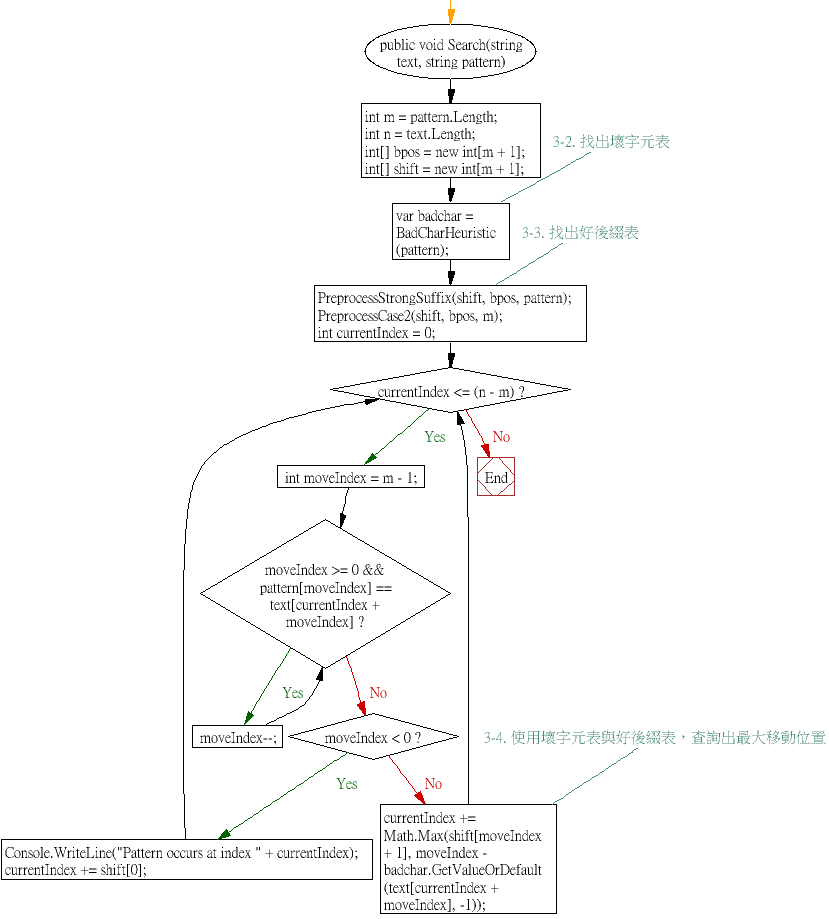
第四部分:Boyer-Moore 演算法 - 實現&圖解:完整版本
Step 1:建構式 - 進入
完整的 Boyer-Moore 演算法會同時使用[壞字元] + [好後綴表] 提高查詢效率:
public BoyerMooreExample(string text, string pattern)
{
Console.WriteLine("3. 第三種方式:混合法 (完整最基本版本的 Boyer-Moore)");
Search(text, pattern);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine();
}
Step 2:主程式 - Boyer-Moore
主程式拆成 4 小部分,其中第 3-2 部分取得壞字元預處理 ; 3-3 部分取得好後綴表
3-4部分是是同時使用 [壞字元] + [好後綴表] ,使用可以跳過最多字元的結果
/// <summary>
/// 3-1. 執行演算法 - 搜尋指定字串
/// </summary>
public void Search(string text, string pattern)
{
int m = pattern.Length;
int n = text.Length;
int[] bpos = new int[m + 1];
int[] shift = new int[m + 1];
// 3-2. 找出壞字元表
var badchar = BadCharHeuristic(pattern);
// 3-3. 找出好後綴表
PreprocessStrongSuffix(shift, bpos, pattern);
PreprocessCase2(shift, bpos, m);
int currentIndex = 0;
while (currentIndex <= (n - m))
{
int moveIndex = m - 1;
while (moveIndex >= 0 && pattern[moveIndex] == text[currentIndex + moveIndex])
moveIndex--;
if (moveIndex < 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pattern occurs at index " + currentIndex);
currentIndex += shift[0];
}
else
{
// 3-4. 使用壞字元表與好後綴表,查詢出最大移動位置
currentIndex += Math.Max(shift[moveIndex + 1], moveIndex - badchar.GetValueOrDefault(text[currentIndex + moveIndex], -1));
}
}
}
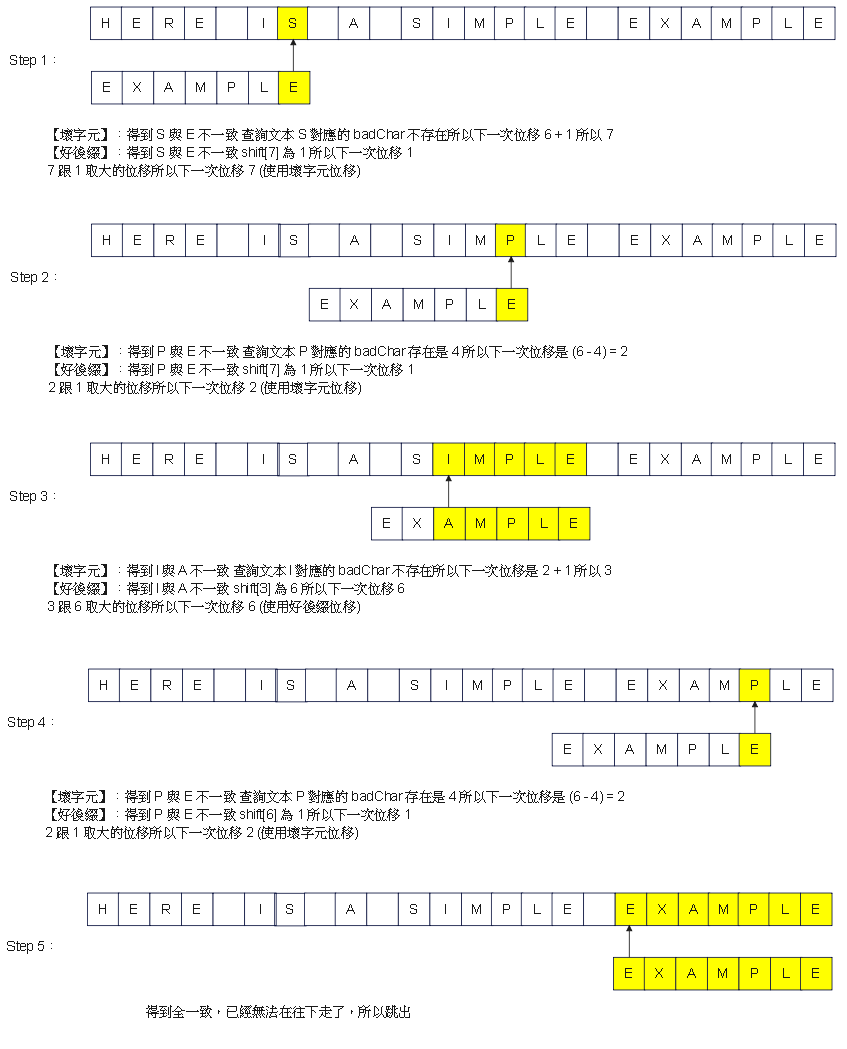
Step 4:圖解
使用文本 : HERE IS A SIMPLE EXAMPLE
搜尋字串 : EXAMPLE
壞字元表 : [6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
好後綴表 : [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 1]
好後綴表變數名稱:shift
Step 4:流程圖
附上完整版本的程式流程圖